You can’t make an omelette without breaking a few eggs, the old saying goes, and it is true for learning how to fix vintage pens. Today, we are going to learn how to restore a lever-filling fountain pen…or re-sac it, as they say. But first, you are going to have to get used to the concept that you’re going to destroy a few pens along the way—even if you’re careful.

Find a few good, cheap vintage pens to practice restoring before experimenting with more expensive models. This deformed Sheaffer Balance 350 is a great starter pen.
When you are starting out, don’t begin with an unrestored version of your grail pen. Find some broken-down cheap pens such as Wearevers, Esterbrooks or even this banana’d Sheaffer 350 Balance. The longer you are on the hunt, the more you will find vintage pens that turn into the shape of bananas. The deformation happens when the pen is left in the sun or near a heater for too long, which warps the plastic/celluloid.
In addition to a good practice pen, you will need some ink sacs, a pair of spark-plug/section pliers, a long dental pick, sac shellac or rubber cement, scissors that can cut through rubber ink sacs, a jar or cup, clean water, polish, a cloth rag, paper towels, a hairdryer, a razor blade and, if at all possible, an ultra-sonic cleaner. You can get most of these items pretty cheaply. One trick of the professionals is to buy a pair of rubber coated spark-plug pliers, instead of formal “section pliers” that you can find on many pen restoration sites. Why? Spark-plug pliers can be had for less than $10 at most auto parts stores. Section pliers are almost always the same, exact pliers but marked up to $20 or $30. In the early days of pen restoration as a hobby in the 1970s and ’80s, a lot of guys used regular pliers and cut off two one-inch sections of hose to cover the teeth of their normal pliers. That’s how I was first taught.
Attempting to keep this simple, I’m going to break this down into what I hope are very simple steps to make this as fun and easy an experience as possible.
-

I like small mustard or baby food jars to use for filling with just enough water to get the pen wet from the tip of the nib to just over the threads of the barrel.
Fill a cup with just enough room-temperature water that you can stick your pen in and go just a little bit over the section and past the cap threads. (Sections are the writing grip into which the nib and feed are inserted in one end.) Let it soak for at least an hour. (Never use hot water.) This leaches out a lot of the dried old ink in the nib and inkfeed, while also potentially softening any glue or shellac used to hold the section tightly into the barrel. Many of the old factory repair manuals encouraged repairmen to use a dab of sac shellac to hold the sometimes loose pressure-fit sections into the barrel. WARNING: Water is necessary, but it also isn’t your friend. Black hard rubbers turn chocolatey brown in water fairly quickly. (An hour might be too long for some rubbers.) Some celluloids get more brittle or discolored when in water too long. Be sure to dry off the pen as soon as you remove it from the water.
2. Use the hairdryer to warm up the space where the section and barrel meet. DO NOT melt the plastic or set the celluloid on fire. All you need is a little warm to the touch. Until you get comfortable, keep the heat to barely noticeable to the touch. Grip the section, and only the section, with your rubber coated pliers. Very gently and slowly begin to twist counter clockwise as you hold the barrel in your other hand. It is common to hear some very scary cracking sounds. Usually, that sound is the petrified rubber ink sac in the pen breaking apart as you open. Sometimes it is the pen barrel breaking. Experience will teach you the difference. If you feel the section coming loose,

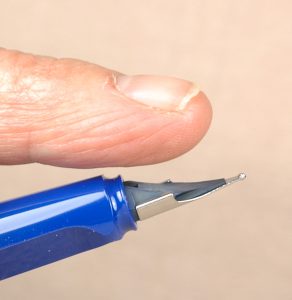
Grip only the section with rubber coated pliers, such as these spark-plug pliers. Don’t grip too tightly, just enough not to let go.
keep twisting slowly and gently. If you do not feel it turning or you feel it actively resisting, stop twisting. Some sections—especially Parker Duofolds and Vacumatics—were threaded into the pen barrels, which is why we usually start with a twist. Most pens of all brands were straight pressure-fit sections. HOWEVER, some brands—especially Wahl-Eversharp, although they were extremely inconsistent—used little pins in the barrel or section to hold the section firmly in place. You CANNOT twist those sections without destroying the barrel or section. If a section resists twisting, hit it with a little more heat and very gently start trying to wiggle it in teeny, tiny side-to-side motions while pulling straight out.
This is the most dangerous part of the entire restoration job. This is where probably 80% of all pens break, if they are going to break. ALSO, celluloid is insanely flammable. DO NOT get it hot. If it catches fire, it burns like a magnesium flare. It is an extremely hot burning flame that burns extremely quickly. Early on, I accidentally set a Vacumatic on fire. It scared the hell out of me, and it was a miracle I didn’t burn down my house. Even after getting it under running water it didn’t go out right away. I had to drop it in the steel sink and flood it to put the fire out. In about 10 seconds, it burned away the majority of the barrel. Be careful with the heat.

Use a razor to scrape the old sac pieces off the section nipple.
3. Once the section is free, scoop out the old sac guts from inside the barrel with the dental pick. Sometimes those guts stick pretty good to the inside of the barrel. A flashlight or gun light can help you see in to make sure you got it all. Do not put water in the barrel to clean out the sac or old ink. This will likely ruin and rust-out the pressure-bar assembly.
4. Use the razor to scrape the remnants of the old ink sac from the nipple of the section. Be careful not to cut yourself or split open the nipple.
5. Fill your ultra-sonic cleaner with clean, room-temperature water. Sometimes a drop or two of ammonia will help badly clogged pens. Put enough water in to completely submerge the cap and section assembly. Before you turn it on, let the cap soak for a minute or so. This allows the water to penetrate the inner cap, where a lot of old ink is usually trapped. After the cap and section have had a minute to soak, turn on the ultra-sonic cleaner for no more than 2 minutes.

If feasible, an ultra-sonic cleaner is the easiest way to remove old ink.
You might not see a lot of “action” with your eyes, but the vibrations are practically violent to the parts that are submerged. It can shake free most of the old ink in two minutes or less. If a cap lip is cracked, I’ve seen some caps crumble in the ultra sonic cleaner. That’s how powerful it is.
NEVER stick your fingers in the ultra-sonic cleaner when it is turned on. It can damage your fingers and their joints. Also, don’t leave your parts in for much longer than two minutes because the cleaner will get hot and potentially damage or discolor your parts.
Turn off the ultra-sonic cleaner, collect your parts and drain the old dirty water. Then rinse the parts under the faucet with room temperature water for a few seconds. Shake the parts dry, and then dry them with a paper towel on the outside. Q-tips are perfect for drying and removing the remaining ink from inside the cap.
6. I like to polish the pen next, especially the nib. It allows me to see any major flaws I might need to work on, such as replacing the nib while the section is exposed. I use a pin-head dollop of MAAS metal polish on a Q-tip to get the nib shining like new. I use the clean side of the Q-tip to wipe off the remaining polish. Then I dip the nib in water and dry it with a clean rag to get off the remaining, invisible polish remnants. I repeat the process with a pea-size drop of MAAS metal polish on the rag and polish up the rest of the pen, rubbing it down several times with the clean parts of the rag…avoiding water.
Every repairman I know seems to have a different process for polishing a pen. The method above is adequate for most pens. Yet, if you’re a detail-oriented person, there are myriad methods of multiple polishes or wet sanding that do a much more factory-fresh looking job. Yet, those methods take up to an hour and are worthy of their own article.

This photo illustrates how to eyeball the spot you need to trim the ink sac.
7. Sizing an ink sac. How detail oriented are you? You can easily research what size sacs went into what pens. You can measure the nipple with a fine ruler using increments of 1/64th of an inch, the way old pen repair manuals did to find the right aperture width of the ink sac. Or, you can eyeball it.
The real trick to eyeballing it isn’t fitting the sac to the nipple but finding the right sac to fit inside the barrel. You do not want the edges of the sac to snug against the inside of the barrel. It is best if the sac can easily slide in and out of the barrel, preferably with a little space all around the sac. If one is to carry a pen in their shirt pocket, the goal is not to transfer body heat through the barrel to the sac and ink, which might effect the interior pressure of the ink in the pen and have it leak a bit on you with a full pen.
Regardless of how you choose the sac size, you will likely need to trim the ink sac before installing it. Most ink sacs are longer than the pen barrels. My rule of thumb is quite literally a rule of thumb. I stick the sac in the barrel as far as it will go. I then pinch the end of the barrel at the threads, with my thumb having just enough reach to go past the threads. Pinching awkwardly down on the sac, right where it exits the barrel, I remove the sac. Gaging where my thumb tip is, I trim the sac at the tip of my thumb. Usually, this allows just enough room for the section and nipple inside the pen so that the sac can be as long as it needs to be. You can double check the length by putting the section and sac next to the empty barrel, as they would fit inside it.

Use Talc to powder and preserve your new ink sac before final re-assembly.
8. Most modern pen restorers use orange shellac to affix the sac to the nipple. Before most of us learned how to make or knew where to find orange shellac for sale, rubber cement was the go-to adhesive. Orange shellac is nearly perfect, as it can harden and still be water soluble. Rubber cement forms a good seal at first but can be more easily effected by heat and aging. Yet, it better fills-in tiny hairline cracks in the nipple, hopefully extending the functional life of the pen. (NEVER use super glues of any kind. The rubber ink sacs will give out long before the super glue ever does and you can ruin the pen by forever getting the section stuck in the barrel…or sticking other wrong parts together.)
On this pen, we painted only the nipple with a thin layer of shellac. Then we slipped the sac over it. After that, we dusted the sac with pure talcum powder, which helps to extend the life of the sac.
9. Fitting the section back into the barrel is the second most dangerous part of the restoration process. Sometimes the barrel opening shrinks while the section is out and cracks open if you put the section back in too quickly or roughly. If the section feels like it is having difficulty going back in, maybe warm up the barrel end a little and gently wiggle the section back into place. Although it doesn’t really matter, I like twist the section into place where the top of the nib is even with the lever on the pen.

Congrats! Your pen is fully restored, looking beautiful and ready to write.
If the section is too loose, you can tighten it up with a tiny cut out of a piece of onion-skin paper. Or, like the old repair manuals, you can use a small drop or two of shellac on the section. Just wipe off the excess shellac and keep it out of the threads.
10. Let the shellac dry. As the shellac is water soluble, I wait about 24 hours before I test the pen with water or ink. Once the shellac is dry and the pen tests well, you’re all done. Congrats!
It took longer to read this article than it likely will take you to restore a pen—at least once you get used to the process. Fixing and writing with vintage pens is my favorite part of the hobby. If you like seeing how things work and getting your hands dirty, you’ll love pen repair. The only thing that improves it for me might be repairing pens while listening to a Cubs game on the radio and nursing a cold beer.
Always feel free to write in with questions. And always remember to go slowly and take your time. It isn’t a race. Enjoy the zen of pen repair, and best of luck to your future projects!
 For the last several years, we have heard about the splendor of the Baltimore Pen Show. This is what we’ve heard: It is well organized by our buddy Bert Oser. It is a premier place to buy and sell premier luxury pens. It is well advertised to the public, and it is becoming the premier pen show in the country.
For the last several years, we have heard about the splendor of the Baltimore Pen Show. This is what we’ve heard: It is well organized by our buddy Bert Oser. It is a premier place to buy and sell premier luxury pens. It is well advertised to the public, and it is becoming the premier pen show in the country.
 Shopping Cart
Shopping Cart